- Revenue Cycle Management
- COVID-19
- Reimbursement
- Diabetes Awareness Month
- Risk Management
- Patient Retention
- Staffing
- Medical Economics® 100th Anniversary
- Coding and documentation
- Business of Endocrinology
- Telehealth
- Physicians Financial News
- Cybersecurity
- Cardiovascular Clinical Consult
- Locum Tenens, brought to you by LocumLife®
- Weight Management
- Business of Women's Health
- Practice Efficiency
- Finance and Wealth
- EHRs
- Remote Patient Monitoring
- Sponsored Webinars
- Medical Technology
- Billing and collections
- Acute Pain Management
- Exclusive Content
- Value-based Care
- Business of Pediatrics
- Concierge Medicine 2.0 by Castle Connolly Private Health Partners
- Practice Growth
- Concierge Medicine
- Business of Cardiology
- Implementing the Topcon Ocular Telehealth Platform
- Malpractice
- Influenza
- Sexual Health
- Chronic Conditions
- Technology
- Legal and Policy
- Money
- Opinion
- Vaccines
- Practice Management
- Patient Relations
- Careers
The Taxman Leaveth: Low, Low Taxes in Early Retirement
It's quite possible to legally pay no federal income tax with a six-figure budget in early retirement.
During our years of wealth accumulation, a.k.a. working, we pay a pretty penny in taxes. We become accustomed to knowing that after a certain point, we might only see about half of each additional dollar earned. Adding up federal & state income tax and property taxes, many physicians will have annual tax bills exceeding $100,000. If you’ve managed to accumulate a sizable nest egg over 20 years or less, you’ve no doubt contributed at least$1 millionto the coffers of the taxman.
Fear not. Much, much lower tax rates are on the horizon for the aspiring early retiree. Let’s crunch some numbers and examine what you might expect to pay when you hang up the stethoscope for the last time.
Take the example of someone likeDr. Benson from the 4 Physicians articlewho was on track to retire with $3 million in about 20 years with $120,000 in annual spending. As you’ll see below, he ended up with $3.3 million. Will he require $120,000 a year in retirement? Of course not. He paid off his $36,000 a year mortgage, he’s no longer contributing to a 529, and his children are off on their own.
To maintain the lifestyle he and his wife have enjoyed, his spending will be closer to $70,000. Since they expect to travel more, let’s give them $80,000 a year for a comfortable retirement. This represents a super-safe 2.4% withdrawal rate. With $100,000 in annual spending, the withdrawal rate would still be a paltry 3%. They can expect to watch their nest egg grow most years in retirement with this level of spending.
Taking a look at how Dr. B arrived here in his early fifties, we see that he wisely has his nest egg spread out among different account types. He maxed out his tax-deferred savings, while contributing to personal and spousal backdoor Roth IRAs. His HSA has grown nicely, and more than a third of his nest egg is in a taxable account. Allow me to display this saving andcompoundingin a handy little spreadsheet. I do like spreadsheets.
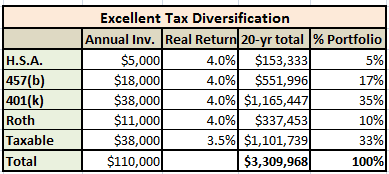
We’re assuming 4% real (inflation adjusted) returns, so spending power is preserved. For the taxable account, I accounted for a half percenttax drag*, so that account has returned 3.5%.
*This tax drag assumes a portfolio of passive index funds with 2% qualified dividends taxed at 25%. The tax on qualified dividends could be as low as 15% if you have no state tax and keep AGI under $250,000, avoiding the 3.8% medicare surcharge. In that best case scenario, the Bensons could have had a 3.7% real return on their taxable account in the working years.
The Bensons, having paid a little over $1 million in federal income tax alone, don’t want to pay that anymore. Like, not at all. Zero. Zilch. Can we get them $80,000 to spend without incurring federal income tax? Sure. Why not aim for $100,000? Plugging some reasonable numbers into Intuit’sTaxCasterusing 2015 tax rates gives us the following results.
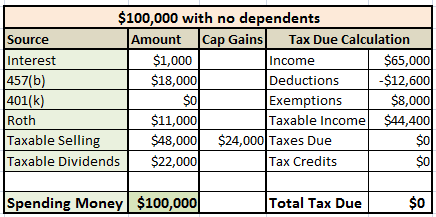
In this example, the Bensons get their spending money from the following sources:
- They receive $1000 in interest from the emergency account where they keep ready cash.
- They set up the 457(b) to deliver $1500 a month, or $18,000 for the year.
- Since they know that they can remove Roth contributions without penalty, they plan on taking out $11,000 a year for the next 20 years.
- They sold $48,000 worth of index funds which had doubled in value, creating $24,000 in capital gains.
- Their $1.1 million dollar taxable fund distributed $22,000 in qualified dividends.
They owe0federal income tax. In fact, with only $44,400 in taxable income, they could have had a much higher taxable income and still paid no income tax. This could be considered a wasted opportunity. Nice going, Bensons. Way to go.
How much more capital gains could they have taken without owing federal income tax?
The Bensons sold a whopping $109,000 worth of mutual funds that had doubled. Their cost basis being $54,500 meant a long-term capital gain of $54,500.
. Why? If you have a taxable income of $74,900 or less in 2015, your long-term capital gains and qualified dividends have a 0% tax rate. If you get lazy or goof up and end up with $75,000 in taxable income, don’t worry, you haven’t fallen off a cliff. You won’t owe 15% on all of your capital gains and qualified dividends, you’ll just owe on the portion that exceeds the limit. If you exceed the limit by $100, you owe $15 in taxes.
Still no tax
In the first 2 examples, we assumed the kids were long gone. Not in college, not dependents. But what it that weren’t the case? What if they were in college, considered dependents, and the Bensons paid $4000 out of pocket towards their education?
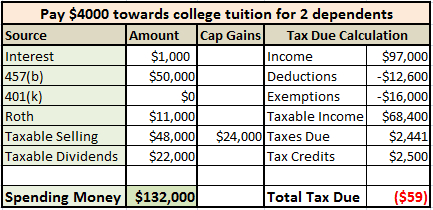
TheAmerican Opportunity Tax Credit (available to married couples with MAGI under $160,000) will match the first $2000 paid toward tuition with a $2000 tax credit (that’s free money, folks) and provide an additional $500 credit for the next $2000. In this case, the Bensons can take a lot more from the 457(b) ordo some Roth conversions from the 401(k), provided it is rolled over to a traditional IRA first.
Rather than increasing the 457(b) withdrawal, they could have maintained it at $18,000 and converted $32,000 of traditional IRA (previously 401(k)) money to a Roth IRA. What is the advantage of doing this? Reducing required mandatory distributions (RMDs) which will be enforced at age 70.5, thereby avoiding future taxable income.
What if the Bensons still had children in junior high when they retired? SayHello to the child tax credit of $1000 per child. The children must live at home, be under 17 years of age, and taxable income (MAGI) must remain below $110,000 for the married joint filers. Easy enough.
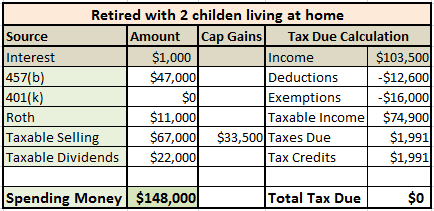
The child tax credit only applies to taxes due, so the Bensons either took more from the 457(b) or did some Roth conversions in December to get their “taxes due” as close to $2000 as possible. Since you most likely will not have the ability to adjust your 457(b) income on an annual basis, it is probably best to use Roth conversions to keep taxable income flexible during early retirement.
Note that in 2 of these examples, the Bensons had spending money exceeding 4% of their nest egg of $3.3 million (= $132,000). It might be OK for them to do so in a year with good market returns, particularly if they are planning on using a variable withdrawal strategy. The point of this exercise is not to show much they can spend each year without depleting their nest egg, it is to show how much money can be made available without paying federal income tax in early retirement.
The take home lessons from this exercise are many:
- You can live well without paying federal income tax in an early retirement scenario.
- It’s important to diversify your retirement dollars among different account types, some of which have already been taxed (Roth, taxable account).
- Roth contributions can be withdrawn without penalty at any age. Growth cannot. Keep track of contributions if you think you might want to access the account prior to age 59.5.
- Keeping taxable income in the 15% bracket makes your long-term capital gains (on equities purchased at least a year ago) and qualified dividends tax free.
- Retiring while your kids are at home or in college will allow you to take advantage of tax credits that are generally not be available to working physicians; they are phased out due to high income.
- We didn’t touch the 401(k) other than for the sake of making Roth conversions. If you feel you will need to access this money before age 59.5, there are a couple ways. One is to retire in the year in which you turn 55 (or 56 — 59). By law, you should have immediate access. Before that age, you can rollover to an IRA and set up Substantial Equal Periodic Payments (SEPP) to access the money without penalty. If you plan well and have monies in other accounts, you probably won’t be touching this money until at least 59.5 or perhaps 70.5 when RMDs become mandatory.
- Social Security never entered the discussion. Again, if you planned like the Bensons, you’re not relying on it and might delay collecting until age 70 to get the maximum dollar benefit.
- If you live in a state with an income tax, expect to pay a few thousand dollars a year in the above scenarios. Tax-Rates.org has a tax calculator that includes state taxes for every state.
- You will not be paying FICA taxes if you have no earned income as was the case with the Bensons.
- There is a net worth above which avoiding federal income tax is no longer possible. You know, Mo Money Mo Problems. It depends on how your dollars are distributed. If you’ve got that much, which I estimate is north of $5 million, paying taxes should be no problem at all. There is also an age at which it becomes unavoidable (70 due to RMDs) unless you’ve managed to convert most or all tax deferred dollars into Roth (or spent it all).
What is the take-home message for you? Do these analyses make you more or less likely to consider an early retirement? How likely is it that the tax code will remain largely intact by the time you will be ready?
