Image IQ: Chest pain, cough, syncope and shortness of breath
An 80-year-old woman who was wheelchair bound due to congestive heart failure was brought to the ED complaining of left-sided chest pain, shortness of breath, cough and syncope. An ECG showed tachycardia. What's your diagnosis?
(©VisualDx)
An 80-year-old woman who was wheelchair bound due to congestive heart failure was brought to the ED complaining of left-sided chest pain, shortness of breath, cough and syncope. An ECG showed tachycardia.
What's your diagnosis?
A. Pulmonary embolism
B. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
C. Pneumothorax
D. Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia
Use the differential builder on VisualDx to guide your decision.
See the next page for the answer
The correct answer is A.) Pulmonary embolism
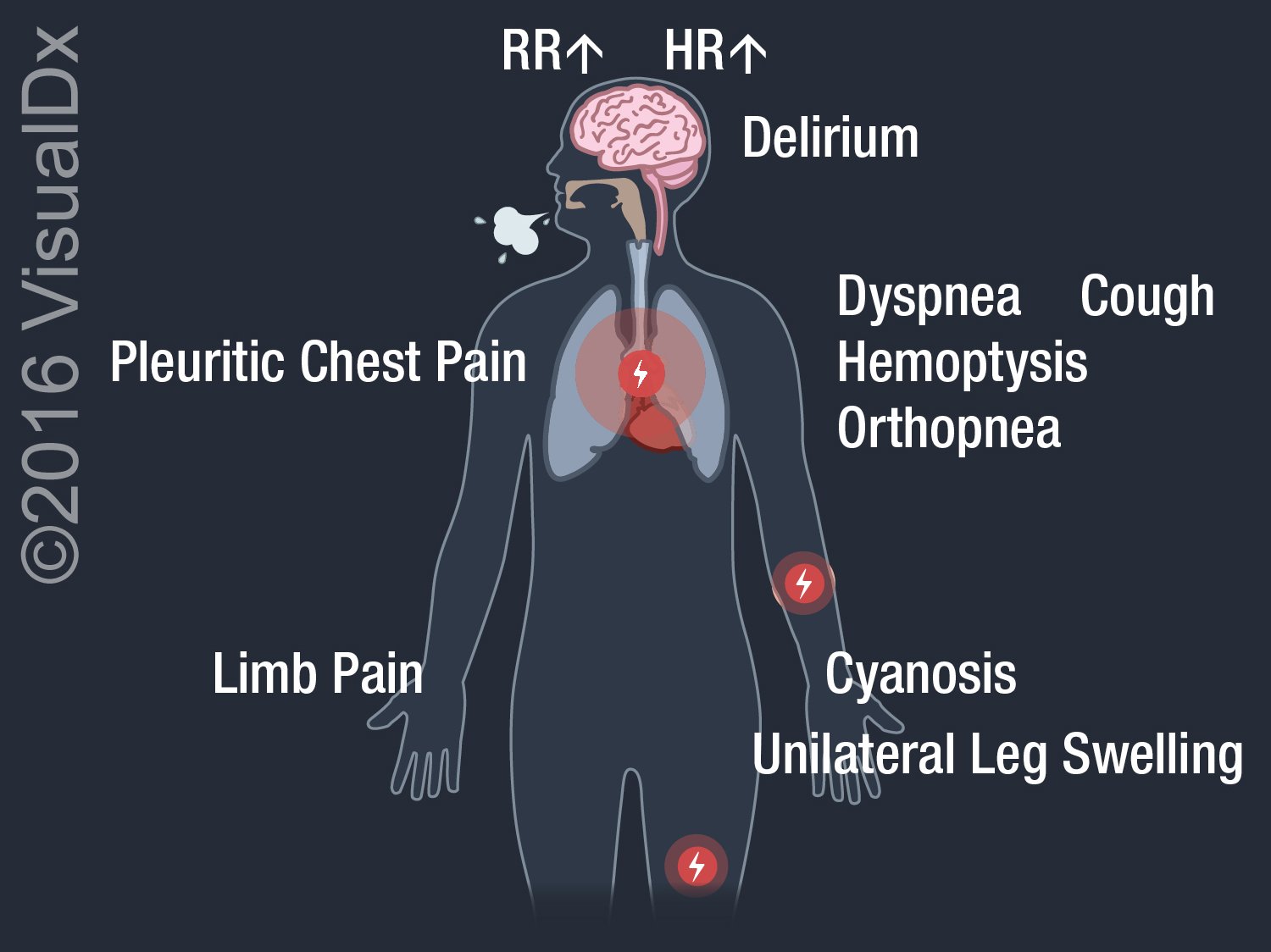
Synopsis: A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that typically originates from thrombi in the deep venous system of the legs and travels to the lungs. It can also originate from deep pelvic veins, rectal veins, the inferior vena cava, the right heart, and the axillary veins. Approximately 10% of cases are fatal.
The clinical presentation depends upon the size, location, number and chronicity of emboli, and the patient's cardiorespiratory reserve. Features include dyspnea and tachypnea, pleuritic chest pain, cough, hemoptysis, pleural effusion, pulmonary infiltrates, cyanosis, syncope, and, in some cases, sudden death (classically pulseless electrical activity [PEA] arrest).
Predisposing factors for PE include history of venous thromboembolism, embolization of struts from inferior vena cava filter, genetic predilection (Factor V Leiden, anti-thrombin III gene mutation, protein C or S deficiency, etc), cancer, trauma, surgery, pregnancy or oral contraceptive use, prolonged immobility, advanced age, obesity, and congestive heart failure.
There are often long-term recurrent risks of another thromboembolism after the first venous thromboembolism.
For more information about pulmonary embolism, including ICD 10 codes, visit VisualDx.