Article
American Heart Association Releases Scientific Statement on Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use in Heart Failure
Sheryl L. Chow, PharmD

In an effort to combat medical misinformation on the subject, the American Heart Association (AHA) has released a new scientific statement centered around the benefits and risks of using complementary and alternative medicines to manage symptoms of heart failure.
Using data published prior to November 2021, the AHA statement encourages providers to discuss use of complementary and alternative therapies and talk about potential medication interactions as well the benefits and potential side effects of use at every visit, noting use of complementary and alternative therapies is a practice among 30% of people with heart failure in the US.
“These products are not federally regulated, and they are available to consumers without having to demonstrate efficacy or safety to meet the same standards as prescription medications,” said Chair of the scientific statement writing committee Sheryl L. Chow, PharmD, an associate professor of pharmacy practice and administration at Western University of Health Sciences and associate clinical professor of medicine at the University of California in Irvine, in a statement. “People rarely tell their health care team about their use of supplements or other alternative therapies unless specifically asked, and they may not be aware of the possibility of interactions with prescription medicines or other effects on their health. The combination of unregulated, readily accessible therapies and the lack of patient disclosure creates significant potential for harm.“
Prepared on behalf of several AHA committees, including the Clinical Pharmacology Committee and Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology, the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, the 27-page documents cites more than 200 references. Following the abstract and introduction, the writing committee provide perspective on global utilization and the influence of social determinants of health on use of these therapies.
A central portion of the document is dedicated to a pair of tables spanning 11 pages providing an overview of clinical efficacy studies of complementary and alternative medicines on heart failure and clinical studies of complementary and alternative medicines that interact with heart failure therapy or worsen heart failure, respectively. Later in the document, the writing committee provides a color-coded graphic listing the complementary and alternative medicines they consider to be potentially harmful, potentially beneficial, and those where safety is uncertain. The items supplements and activities included in these categories are detailed below.
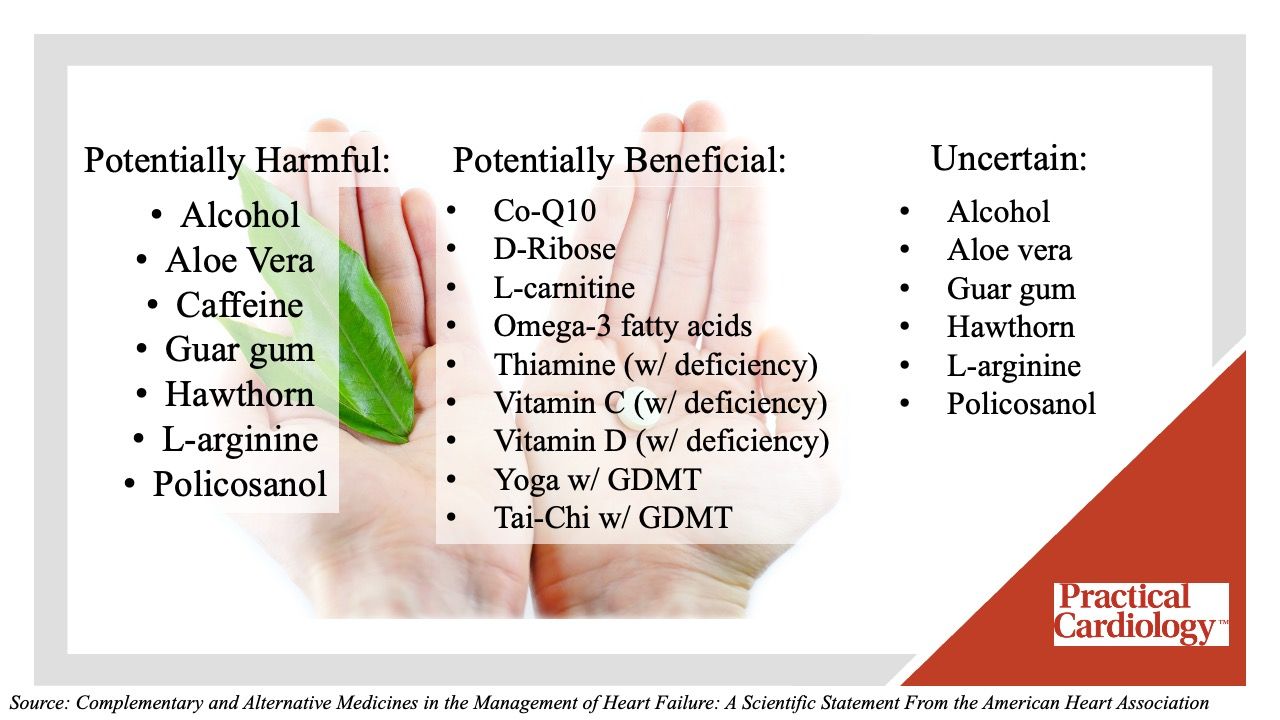
“Overall, more quality research and well-powered randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the risks and benefits of complementary and alternative medicine therapies for people with heart failure,” Chow added. “This scientific statement provides critical information to health care professionals who treat people with heart failure and may be used as a resource for consumers about the potential benefit and harm associated with complementary and alternative medicine products.”
This document, titled “Complementary and Alternative Medicines in the Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association,” was published in Circulation.




