Biologic Therapies Benefit Psoriasis Patients with Depression
Biologic therapies, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, can potentially mitigate symptoms of depression and insomnia in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
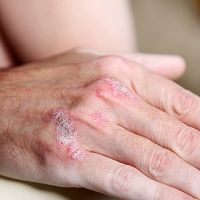
Biologic therapies, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, can potentially mitigate symptoms of depression and insomnia in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
The study, published in Medicine, investigated the effects of biologics on psoriasis patients’ psychological symptoms and wellbeing.
According to the National Psoriasis Foundation and prior studies, psychological symptoms in psoriasis patients are more common than in patients with other skin-disfiguring diseases, and may be as prevalent as in other major clinical diseases like cancer and diabetes.
As such, researchers from Chinese medical and research institutions identified 980 patients with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis who had received treatment with biologics like TNF inhibitors from 2009 to 2012.
The team wanted to assess and compare the rates of such patients undergoing treatment for depression and insomnia before and after biologic therapy.
The study results indicated that before beginning biologic therapy, nearly 20% of patients were regularly taking antidepressants. However, two years of treatment with biologics showed an approximately 40% decrease in the prevalence of antidepressant use.
Additionally, patients younger than 45 on biologic therapy who were not diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis exhibited a significant reduction in depression and insomnia compared to other patients.
The authors concluded, “The results suggest that biologic therapy may be associated with reduced rates of depression and insomnia, and a reduced rate of regular antidepressant use in psoriasis patients.”